Choosing the right business internet can be a challenge. But it’s so important as almost every task your business does each day relies on having a good and fast connection.
This guide is here to help. Here’s what we’ll cover:
Types of Business Internet Connections
Here's a breakdown of the various connection types available:

DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
While DSL might seem dated in some parts of the world, in certain regional and remote areas of Australia, it's still a relevant choice. It operates over regular telephone lines, providing a balance of cost and performance. However, as the NBN rollout continues, more advanced options are becoming available to replace traditional DSL.
Cable
Before the Business NBN, many urban areas, especially in major cities like Melbourne and Sydney, relied on HFC (Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial) cable. The NBN has taken over a lot of this infrastructure, upgrading it to be part of their multi-technology mix.
Fibre (Fiber-Optic)
In the NBN context, this is often referred to as FTTP (Fibre to the Premises). It's the gold standard for speed and reliability, with light signals transmitting data through thin glass strands. Many businesses aim for this connection, though its rollout is limited by the NBN's multi-technology approach.
NBN (National Broadband Network)
The NBN offers a range of technologies, which businesses need to navigate:
FTTP (Fibre to the Premises)
Direct fibre connection to the business, offering the highest speeds.
FTTC (Fibre to the Curb)
Fibre to the street's edge, with existing copper lines covering the final stretch.
FTTN (Fibre to the Node)
Fibre to a nearby cabinet, with existing copper lines connecting businesses.
Fixed Wireless & Satellite
For remote and rural areas, providing connectivity where traditional wired solutions aren't feasible.
HFC (Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial)
Utilises existing cable TV lines, upgraded to fit into the NBN's network.
Enterprise Ethernet
In Australia, this is often delivered over the NBN's infrastructure, providing businesses with a dedicated, high-performance connection. It's especially crucial for large enterprises or those with heavy data needs.
Fixed Wireless
Separate from the NBN's fixed wireless offering, some private providers offer fixed wireless solutions, especially in areas where traditional wired options are lacking. They're beneficial for bridging the connectivity gap in regional areas.
Satellite
For businesses in extremely remote areas, satellite might be the only option. The NBN’s Sky Muster satellite service is designed to cater to these remote regions.
T1 & T3 Lines
While these dedicated lines were more prominent in the past, they've largely been replaced by fibre and NBN solutions in Australia. However, some legacy connections might still exist in specific locations.
Comparison of Business Internet Types
We graded the performance of each business internet type across specific criteria:
- Excellent performance or suitability.
- Above average, with minor limitations.
- Average performance, with noticeable limitations.
- Below average, with significant limitations.
| Internet type | Speed | Reliability | Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSL | C | B | B | Small business in limited access areas. |
| Cable | B | B | B | Small to medium business in urban areas. |
| Fibre (Fibre-Optic) | A | A | C | Tech-Heavy business, online operations. |
| NBN | A | A | C | Tech-Heavy business, online operations. |
| Enterprise ethernet | A | A | D | Large corporations requiring high-speed consistency. |
| Fixed wireless | C | C | B | Rural business without wired infrastructure. |
| Satellite | D | C | C | Extremely remote businesses. |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Business ISP
Speed & Bandwidth:
Determine the speeds the ISP offers and whether they align with your business needs. Consider both download and upload speeds, especially if your business frequently transfers large files or uses cloud services.
Reliability & Uptime:
Research the ISP's track record for reliability. Consistent internet access is vital, so look for ISPs that offer high uptime guarantees, often reflected as a percentage (e.g., 99.9% uptime).
Type of Connection:
ISPs offer various connection types like DSL, fibre-optic, satellite, and more. Understand the benefits and limitations of each to choose what's best for your location and needs.
Scalability & Future-Proofing:
Ensure the ISP can accommodate growth. As your business expands or technology evolves, you'll want an ISP that can easily upgrade your service.
Cost & Contract:
Examine the pricing structure, including any setup fees, monthly costs, equipment rental fees, and potential termination fees. Also, review the contract length and terms to ensure flexibility.
Customer & Technical Support:
Prioritise ISPs that offer robust customer support. Responsive, 24/7 technical support can be invaluable, especially when facing connection issues or during critical business operations.
Security Features:
Inquire about built-in security measures the ISP offers, such as firewalls, anti-malware, DDoS protection, and VPN services.
Coverage & Availability:
Ensure the ISP provides consistent and high-quality service in your business's location. This is especially crucial for businesses in more remote or rural areas.
Additional Services:
Some ISPs offer bundled services like VoIP, email hosting, or cloud storage. These can provide value but ensure you're not paying for services you don't need.
Reputation & Reviews:
Lastly, take the time to research customer reviews and feedback. Real-world experiences can provide insights into the ISP's quality of service, support responsiveness, and overall customer satisfaction.
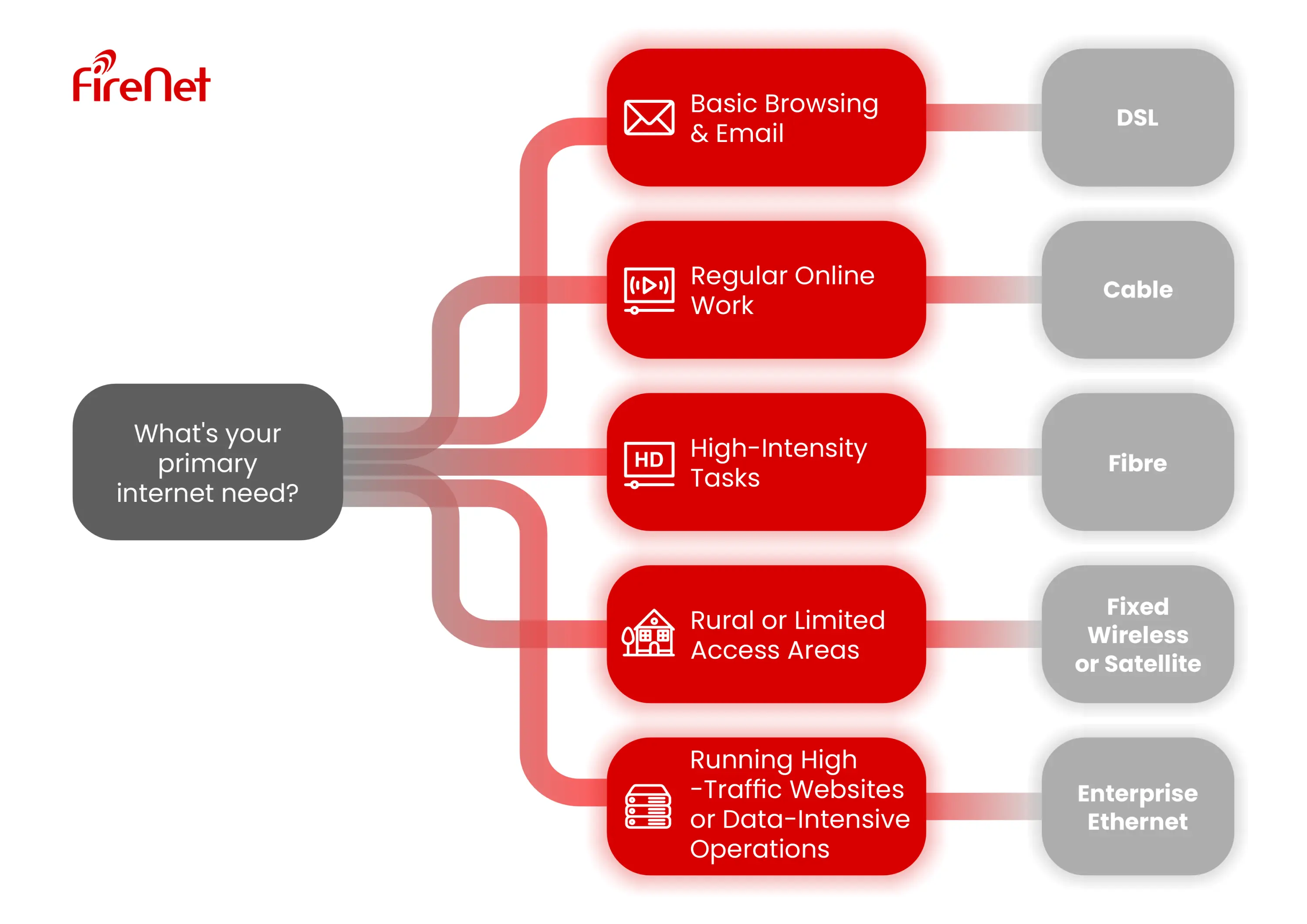
How Much Internet Speed Does Your Business Need?
The flow chart above provides a general guideline. It's crucial to consider the concurrent users and tasks, peak usage times, and future growth when choosing a suitable speed and internet type.
For instance, if multiple employees are video conferencing simultaneously, the required bandwidth multiplies. Always consult with an ISP or IT expert for tailored recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Business Internet
You can use online tools like speed tests that check how fast data travels to and from your device.
Bandwidth is the maximum rate of data transfer across a network.
Upload speed is how fast you send data from your device to the internet, while download speed is how fast you get data from the internet to your device.
Share this post